Imagine you have important company information, and your employees need to access it using their personal Android phones or tablets. Android Device Trust is like a super-smart security guard for these devices. Before it lets any Android device connect to your company's sensitive data, this 'security guard' checks if the device is safe and meets your company's security rules. It keeps checking this continuously, not just once.
This 'Ultimate Guide' will explain exactly what Android Device Trust is, why it's so important for protecting your business, and why you should use it. Understanding this is key to keeping your company's information secure in a world where mobile devices are everywhere. Solutions like Nomid MDM make setting up this kind of 'security guard' simple and effective.
The Problem: The Escalating Challenge of Untrusted Android Devices
The modern enterprise environment is a complex tapestry of company-owned devices, employee-owned devices (BYOD), and third-party contractor devices, all potentially accessing sensitive corporate data. This diversity, while boosting productivity and flexibility, presents a formidable security challenge for IT operations and security managers.
The Unseen Risks in Your Mobile Fleet
Many organizations lack granular visibility into the security posture of each Android device. Are they updated with the latest security patches? Are there malicious apps lurking undetected? Is the device rooted or jailbroken, bypassing built-in security mechanisms? Without answers to these questions, every connection is a potential vulnerability. This lack of trust can lead to:
- Data Breaches: Unsecured or compromised devices can become gateways for attackers to steal sensitive company information, customer data, or intellectual property.
- Compliance Violations: Industries like Healthcare (HIPAA) and Finance (PCI DSS), and general regulations like GDPR, mandate stringent data protection. Untrusted devices put compliance at serious risk, leading to hefty fines and reputational damage.
- Operational Disruptions: Malware or ransomware introduced via an untrusted device can cripple operations, leading to significant downtime and financial loss.
Statistics Highlighting the Mobile Threat Landscape
The scale of the problem is underscored by recent cybersecurity research:
- Mobile malware attacks are continuously evolving and increasing in sophistication.
- A significant percentage of data breaches can be traced back to compromised mobile devices.
- Many employees use personal devices for work, often without adequate security configurations, widening the scope for android security for business failures.
This scenario creates a constant state of anxiety for IT asset managers and technology decision-makers. The core issue isn't just about managing devices; it's about establishing verifiable trust in an increasingly Zero Trust world. The question "what is android device trust" moves from a technical query to a critical business imperative.
"In a mobile-first enterprise, an untrusted device isn't just a risk; it's an open invitation for a security incident. Verifiable trust is non-negotiable."
Current Solutions and Their Limitations: The Patchwork of Mobile Security
Organizations have traditionally employed various methods to secure their Android fleets, but these often fall short in the face of evolving threats and the complexity of modern mobile ecosystems.
Common Approaches to Android Security:
- Basic MDM Policies: While essential, traditional Mobile Device Management (MDM) solutions might focus primarily on configuration and inventory, sometimes lacking the deep, real-time trust assessment capabilities needed. Our guide, "Top Benefits of Using an MDM Solution for Your Business: A Detailed Analysis," covers what a comprehensive MDM should offer.
- Password Policies and Encryption: Forcing strong passcodes and enabling device encryption are foundational but don't guarantee a device isn't compromised at a deeper level (e.g., malware operating with user privileges).
- Antivirus/Anti-malware Apps: These provide a layer of defense but may not catch all threats, especially zero-day exploits or sophisticated attacks that evade signature-based detection.
- VPNs for Network Security: VPNs secure data in transit but don't address the security state of the endpoint device itself. A compromised device on a VPN is still a compromised device.
- Manual Checks and Compliance Audits: These are time-consuming, error-prone, and provide only a point-in-time snapshot of device health, not continuous assurance against dynamic threats.
Limitations and Customer Pain Points:
While these methods offer some protection, they often create a fragmented and reactive security posture. Customers frequently face:
- Lack of Real-time Visibility: Difficulty in knowing the current trust status of all connected devices dynamically.
- Inconsistent Enforcement: Policies might be applied differently across various device types or ownership models (corporate vs. BYOD), creating security gaps.
- User Experience Friction: Overly restrictive policies that don't adapt to context can hinder productivity and lead to user dissatisfaction or workarounds that bypass security.
- Scalability Issues: Manually verifying and managing trust for hundreds or thousands of devices is impractical and doesn't scale with business growth.
- Reactive vs. Proactive Security: Many solutions react to threats after they've been detected, rather than proactively preventing untrusted devices from accessing resources in the first place.
- Integration Challenges: Getting different security tools to work together seamlessly to provide a unified view of device trust can be a major hurdle, leading to siloed information.
These limitations highlight the need for a more integrated, intelligent, and continuous approach to device security – an approach embodied by Android Enterprise Device Trust principles. The transition towards a zero trust android framework is becoming essential.
Demystifying Android Device Trust: Core Concepts and Comparisons
Before diving into how Nomid MDM champions Android Device Trust, it's crucial to understand its fundamental concepts and how it relates to existing device management paradigms.
What Exactly is Android Device Trust?
At its core, Android Device Trust is not a single product but a comprehensive security framework. It involves a set of technologies, processes, and policies designed to continuously assess an Android device's security posture against a predefined baseline. If the device meets these criteria (is "trusted"), it's granted access to corporate resources. If it doesn't, access can be limited or blocked entirely. This verification is dynamic and ongoing, not a one-off check at enrollment. It aims to answer the critical question: "Can this specific Android device, in its current state, be trusted with company data right now?"
Device Trust vs. Device Management Models
It's important to distinguish Android Device Trust from device management models like BYOD, COPE, or COBO. Device Trust is a security overlay that enhances security across all these models:
- BYOD (Bring Your Own Device): Employees use their personal Android devices for work.
- Challenge: Balancing user privacy with corporate security.
- Device Trust Role: Verifies the security hygiene of the personal device (e.g., no malware, up-to-date OS, work profile integrity if used) before allowing access to work apps and data. This ensures BYOD security without inspecting personal data, often leveraging Android Enterprise work profiles to separate work and personal spaces.
- COPE (Corporate Owned, Personally Enabled): Devices are company-owned but allow for personal use.
- Challenge: Ensuring personal use doesn't compromise corporate security.
- Device Trust Role: Continuously monitors the device for risky configurations or apps, even those installed for personal use that might impact the device's overall security posture.
- COBO (Corporate Owned, Business Only): Devices are company-owned and restricted to business use.
- Challenge: Ensuring devices remain compliant and haven't been tampered with, even under strict control.
- Device Trust Role: Provides the highest level of assurance by constantly checking for deviations from the corporate baseline, unauthorized changes, or signs of compromise. Essential for COPE COBO security.
Management Model | Description | Key Challenge | How Android Device Trust Applies |
|---|---|---|---|
BYOD | Personal devices, work use | Privacy vs. Security | Verifies device health (OS, malware, work profile) before granting access to corporate data, ensuring secure work container. |
COPE | Corporate-owned, personal use allowed | Personal use risks to corporate security | Monitors overall device integrity, flagging risky apps/configs from personal use that could impact the device. |
COBO | Corporate-owned, business-only | Maintaining strict compliance, anti-tampering | Continuously validates against baseline, detects unauthorized changes, ensures highest security level for dedicated work devices. |
Android Device Trust and Zero Trust Architecture
Android Device Trust is a fundamental component of a Zero Trust security strategy for mobile endpoints. Zero Trust operates on the principle of "never trust, always verify." In this model:
- No device is trusted by default, regardless of whether it's company-owned or on the corporate network.
- Every access request from any device is authenticated and authorized based on the device's current trust level and other contextual factors (user identity, location, resource sensitivity).
- Trust is continuously reassessed. A device trusted a minute ago might not be trusted now if its security posture changes. Implementing zero trust android security relies heavily on the signals and continuous verification provided by a robust Device Trust framework.
Key Pillars of Device Trust Assessment
A device's "trustworthiness" is typically determined by evaluating several signals, including (but not limited to) those outlined by Android Enterprise. For a detailed list of available signals that can be leveraged, see the official Android Enterprise Device Trust signals documentation.
- Device Integrity: Is the OS unmodified? Is it rooted/jailbroken? Is hardware attestation available?
- Security Configuration: Is encryption active? Is a strong passcode set? Are security patches up-to-date?
- Threat Detection: Is malware present? Is Google Play Protect active and reporting issues?
- Network Security: Is the device connected to a known-risky Wi-Fi network?
- Application Security: Are there sideloaded or unauthorized apps? Do installed apps have excessive permissions?
- MDM Compliance: Is the device actively managed and compliant with MDM policies?
Key Use Cases for Android Device Trust
Understanding the concept of Android Device Trust is one thing; seeing its practical application is another. This framework isn't just a theoretical security measure; it solves real-world business challenges across various scenarios:
1. Secure BYOD for a Hybrid Workforce
- Scenario: Office workers, salespeople, and executives increasingly use their personal Android devices (BYOD) to access corporate email, documents, and applications, whether in the office, at home, or on the road.
- Device Trust Solution: Android Device Trust, enforced by an MDM like Nomid, verifies that these personal devices meet essential security baselines (e.g., up-to-date OS, active screen lock, no malware) before granting access to sensitive data. This is often achieved by ensuring the integrity of a work profile, keeping corporate data separate and secure without infringing on personal privacy.
- Benefit: Enables employee flexibility and productivity while mitigating risks associated with unmanaged or compromised personal devices accessing corporate assets.
2. Fast & Secure Onboarding/Offboarding for Contractors & Temporary Staff
- Scenario: Organizations frequently engage contractors, freelancers, or temporary staff who need quick access to specific company resources for a limited time, often using their own devices.
- Device Trust Solution: Device Trust allows IT to quickly assess the security posture of a contractor's Android device. Access can be granted swiftly if the device meets predefined trust criteria, and automatically revoked or limited when the contract ends or if the device becomes non-compliant.
- Benefit: Streamlines onboarding, reduces IT overhead for temporary staff, and ensures corporate data isn't exposed on potentially insecure third-party devices once their engagement is over.
3. Real-Time Threat Response & Automated Compliance
- Scenario: A device becomes infected with malware, or a user disables a critical security setting (like encryption or screen lock).
- Device Trust Solution: A continuous Device Trust assessment, powered by Nomid MDM, can detect these changes in real-time. If a device's trust level drops below an acceptable threshold, automated actions can be triggered – such as blocking access to critical apps, quarantining the device, notifying the user and admin, or even wiping corporate data if necessary.
- Benefit: Enables rapid response to emerging threats and policy violations, minimizing the window of vulnerability and automating compliance enforcement.
4. Protecting Sensitive Data for Field Service Operations
- Scenario: Field service technicians in industries like healthcare, logistics, or utilities use Android tablets or rugged devices to access work orders, customer data, and technical manuals in diverse, often unsecured environments.
- Device Trust Solution: Ensures these critical devices are always compliant with security policies (e.g., full-disk encryption, restricted app installations, secure network connections only). If a device is lost or stolen, its trust status can be immediately revoked, and remote wipe commands can be issued.
- Benefit: Safeguards sensitive operational and customer data on mobile endpoints that are crucial for business operations but operate outside the traditional office perimeter.
5. Ensuring Device Compliance in Regulated Industries
- Scenario: Companies in sectors like finance (PCI DSS), healthcare (HIPAA), or government have strict regulatory requirements for data protection and device security.
- Device Trust Solution: Android Device Trust provides the mechanisms to enforce and continuously audit these specific compliance controls on all Android devices. Detailed logging of device posture and access attempts helps in generating compliance reports.
- Benefit: Helps organizations meet stringent regulatory mandates, avoid hefty fines, and demonstrate due diligence in protecting sensitive information.
Nomid MDM's Approach: Establishing Comprehensive Android Device Trust
Nomid MDM addresses the limitations of traditional mobile security by providing a platform built on the principles of Android Device Trust. Our mission is "To provide fast, secure Android control for IT operations with less complexity and more productivity," and this philosophy is at the heart of how we help you ensure every Android device is verified and secure before accessing your critical business systems.
How Nomid MDM Enables Android Device Trust:
Nomid MDM integrates key indicators and features that align with Android Enterprise Device Trust, offering a robust framework for continuous verification. We leverage a comprehensive set of signals from the device to build a dynamic trust score. As Google outlines, Android Enterprise Device Trust "helps enterprises of all sizes protect devices and the network by enhancing verification across all Android devices used for work (managed and unmanaged) based on multiple indicators." (Source: Google Blog)
Nomid MDM is designed to work with these signals, and as Google continues to evolve capabilities, such as those available through the Android Management API's Device Trust integration (per Google's Device Trust API documentation), Nomid is incorporating such advancements to provide cutting-edge security.
Key indicators that Nomid MDM utilizes, in line with Android Enterprise guidelines (see Device Trust from Android Enterprise: Key device signals and the more general list of signals in their developer documentation), include:
- Device Model and Make: Ensuring the hardware itself is recognized and approved.
- Management State: Verifying that the device is correctly enrolled and managed by Nomid MDM.
- Network Status: Assessing the security of the network connections (e.g., flagging risky Wi-Fi).
- Security Patch Level: Confirming the device has the latest OS and security updates.
- Disk Encryption Status: Ensuring device storage is encrypted to protect data at rest.
- OS Version and Pending OTAs: Identifying outdated OS versions or pending critical updates.
- Screen Lock and Quality: Enforcing strong screen lock mechanisms.
- Play Protect Status: Verifying that Google Play Protect services are active and scanning for threats.
Benefits of Nomid MDM for Device Trust:
- Fastest Deployment Speed on the Market: Quickly enroll and secure your entire Android fleet, establishing trust from day one. Our "Out-of-box setup experience" and "Automated device provisioning" make this a reality.
- Intuitive Platform for Android Device Management: Our "Centralized management console" provides a clear view of each device's trust status, simplifying complex security tasks.
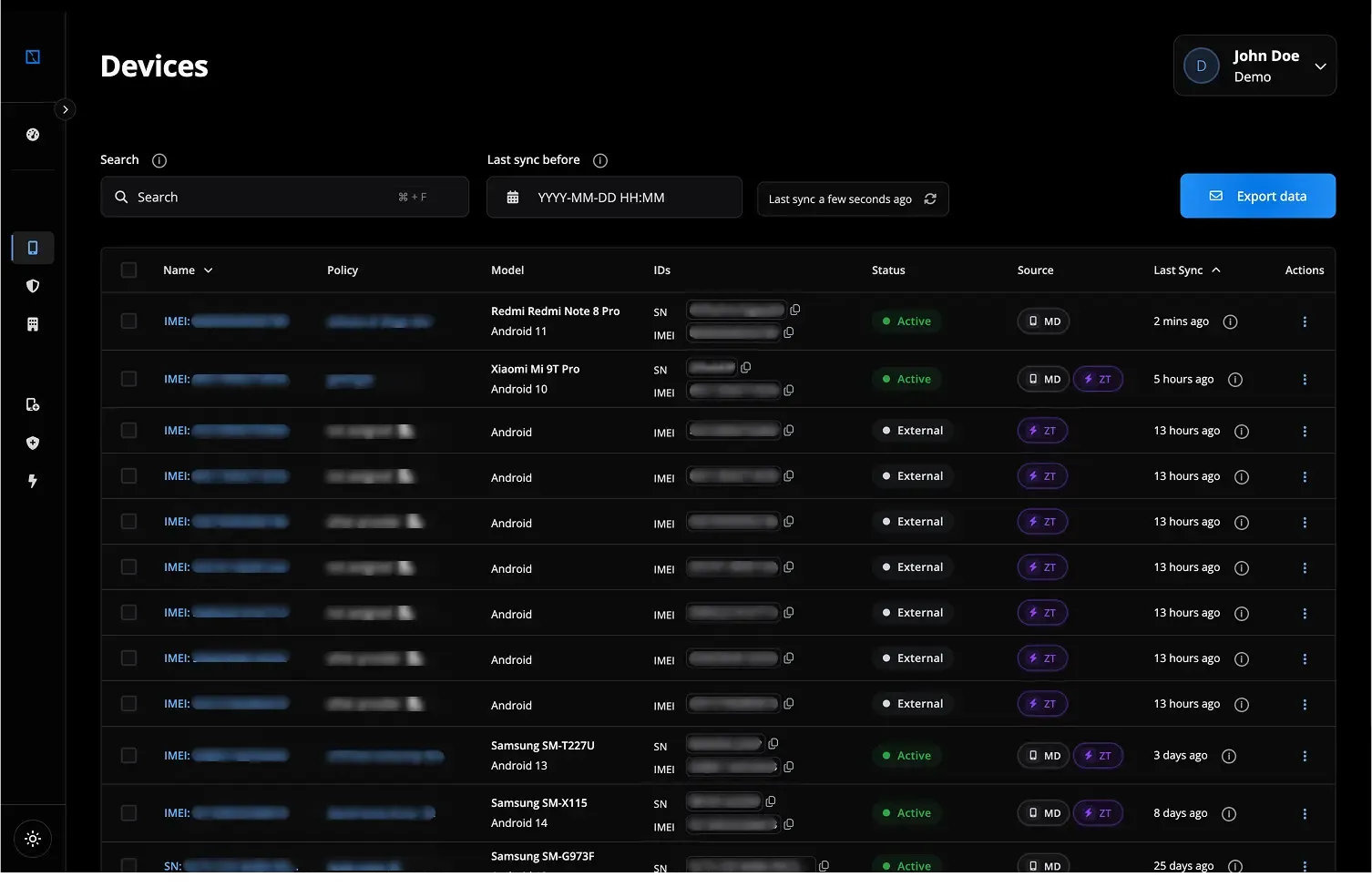
- Enterprise-Grade Security Features: Implement "Advanced security policy enforcement," including real-time checks for compliance and trust indicators.
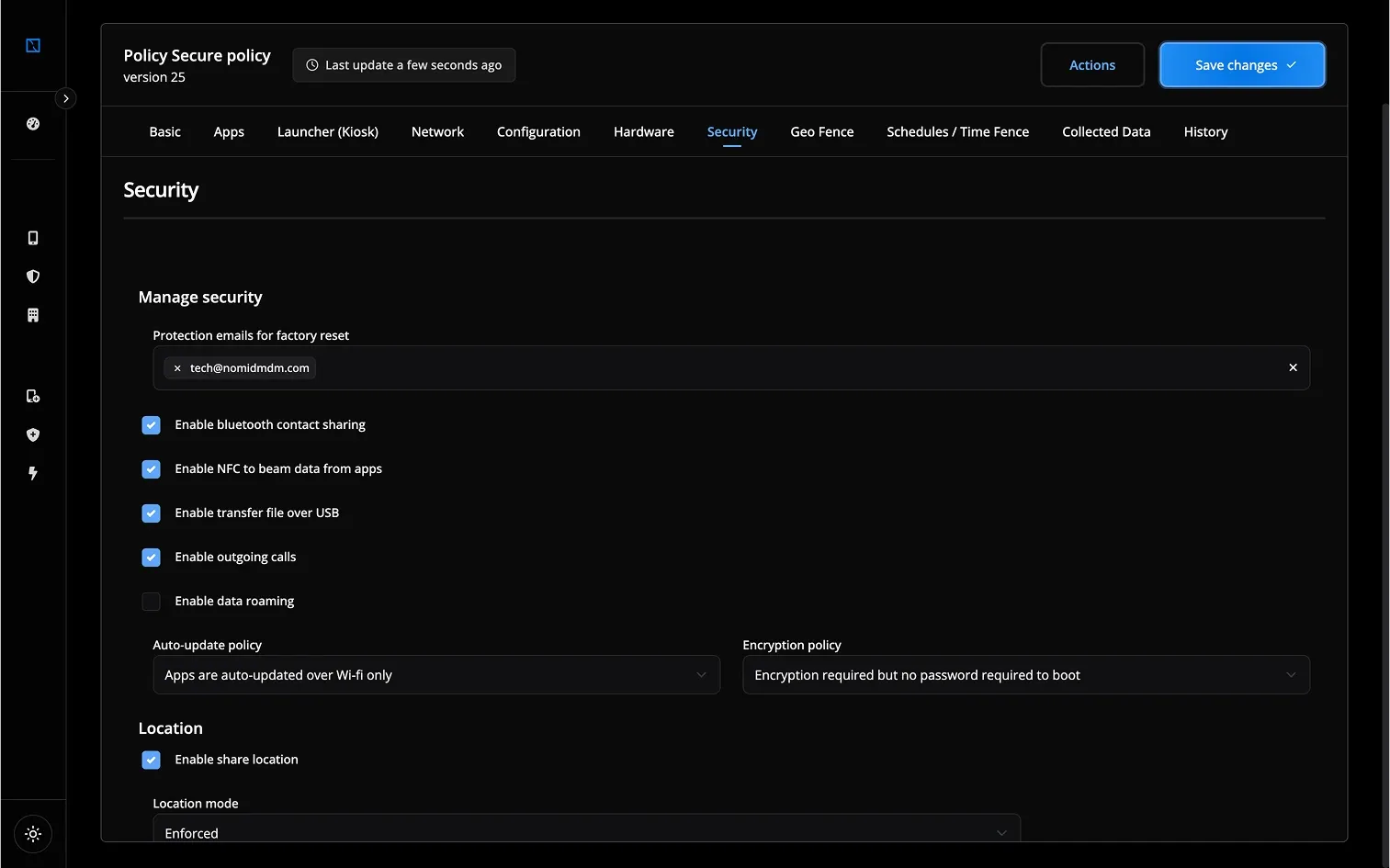
- Real-time Device Monitoring and Control: Proactively identify and remediate untrusted devices with features like "Remote lock, wipe, and reset" and "Real-time device location tracking."
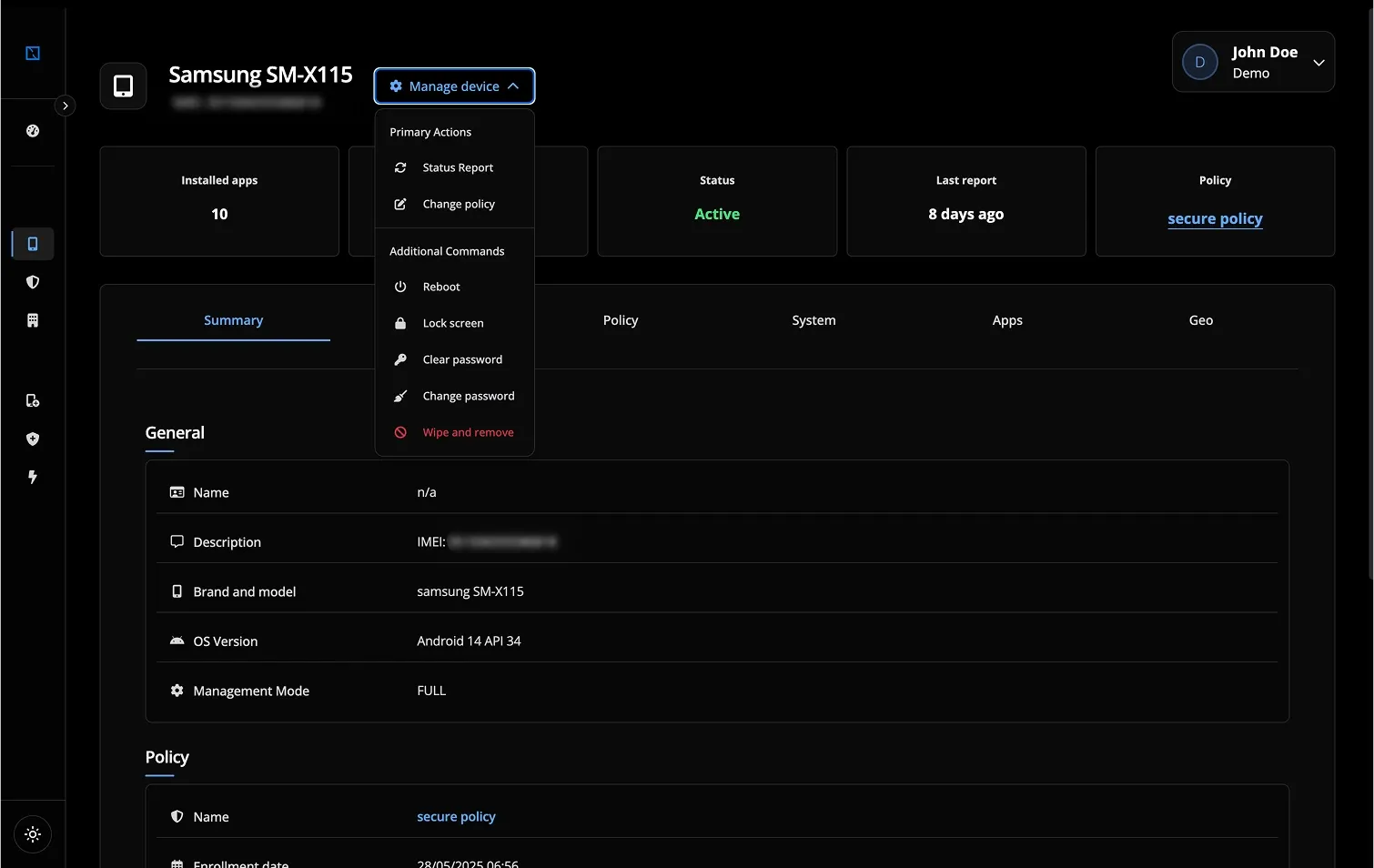
- Support for Key Industries: We understand the unique needs of sectors like Field Service, Education, Logistics, Retail, Manufacturing, and Healthcare, tailoring trust parameters accordingly.
By focusing on these elements, nomid mdm android trust capabilities shift your security posture from reactive to proactive, ensuring that only verified and compliant devices can access your corporate data.

Implementation and Best Practices: Your Roadmap to Android Device Trust with Nomid MDM
Implementing a robust Android Device Trust strategy requires more than just technology; it involves a clear plan and adherence to best practices. Nomid MDM is designed to simplify this journey for IT Operations, IT Asset Managers, and Security Managers.
Step-by-Step Guidance:
- Define Your Trust Policies:
- Identify the minimum security baseline for all Android devices (e.g., OS version, patch level, app restrictions, Play Protect enabled).
- Determine different trust levels and corresponding access rights based on user roles, data sensitivity, and device ownership model (BYOD, COPE, COBO).
- Nomid MDM allows for "Bulk configuration deployment" to easily apply these policies across device groups.
- Enroll Your Devices:
- Utilize Nomid MDM's "Automated device provisioning" (like Zero-Touch Enrollment) and "Out-of-box setup experience" for seamless enrollment.
- Ensure all devices accessing corporate resources are managed and their trust posture can be assessed.
- Configure Trust-Based Access Controls (Conditional Access):
- Use Nomid MDM to enforce access decisions based on real-time trust assessments.
- Set up conditional access policies: if a device falls below a defined trust threshold (e.g., due to outdated patches, detected malware, or disabled security settings), automatically restrict access to sensitive apps or data, notify the user/admin, or quarantine the device.
- Monitor Continuously:
- Leverage Nomid MDM's "Real-time device monitoring and control" and "Compliance monitoring dashboard."
- Regularly review device trust status, security alerts, and compliance reports to identify trends and potential risks.
- Automate Remediation:
- Configure automated actions for non-compliant or untrusted devices. Examples: forcing OS updates, prompting for malware removal, locking the device, selectively wiping corporate data ("Remote lock, wipe, and reset"), or revoking access certificates.
- Educate Your Users:
- Communicate the importance of device security and their role in maintaining it (e.g., accepting updates promptly, not disabling security features).
- Provide clear guidelines on acceptable use, app downloads from trusted sources, and reporting suspicious activity.
- Regularly Review and Update Policies:
- The threat landscape and business needs are constantly evolving. Revisit your trust policies and Nomid MDM configurations at least quarterly to adapt to new android security for business challenges, Android Enterprise updates, and emerging threats.
Compliance Considerations:
- Industry Regulations: Align your Android Device Trust strategy with specific industry requirements (e.g., HIPAA, GDPR, PCI DSS). Nomid MDM's "Advanced security policy enforcement" and detailed logging help meet these needs.
- Data Privacy: Clearly communicate to users (especially in BYOD scenarios) what device information is being monitored for trust assessment, ensuring transparency and adherence to privacy norms. Focus on the security state, not personal content.
- Audit Trails: Utilize Nomid MDM's reporting features to maintain comprehensive audit logs of trust assessments, policy enforcement, and remediation actions for compliance verification and incident response.
By following these steps, organizations can effectively implement and maintain a strong what is android device trust framework, significantly enhancing their mobile security posture.
"Proactive trust verification via Android Device Trust isn't just a feature; it's the foundation of modern mobile security. With Nomid MDM, it becomes an actionable, scalable strategy."
Conclusion: Secure Your Mobile Future with Android Device Trust and Nomid MDM
The question of what is android device trust is no longer a niche concern for IT specialists but a central pillar of enterprise security strategy in 2025. As Android devices continue to be pivotal for business operations across key industries like Field Service, Healthcare, and Logistics, ensuring their trustworthiness is paramount. Failing to do so exposes organizations to significant risks, including data breaches, compliance penalties, and operational disruptions.
This guide has highlighted the limitations of traditional security approaches and underscored the necessity of a continuous, indicator-based trust model, as championed by Android Enterprise Device Trust and aligned with Zero Trust principles. Nomid MDM provides the tools and platform to implement this model effectively, offering:
- Deep Visibility: Understand the real-time security posture and trust level of every Android device.
- Proactive Control: Enforce dynamic, trust-based access policies and automate responses to untrusted devices.
- Simplified Management: Streamline complex security tasks with an intuitive interface designed for IT efficiency.
- Rapid Deployment: Secure your fleet quickly and establish trust from day one.
By partnering with Nomid MDM, you can confidently answer "yes" to the question "Are our Android devices secure and trustworthy?". Don't wait for a security incident to highlight the gaps in your mobile defense. Take proactive steps today to implement a robust Android Device Trust framework.

Ready to elevate your Android security?
Discover how Nomid MDM can help you achieve comprehensive device trust. Start Your Free Trial to experience our intuitive platform firsthand and see why we offer the fastest deployment speed on the market.
Start Free TrialWritten by
David Ponces
Enjoying this article?
Get more insights on mobile device management delivered to your inbox.
Share this article
Tags
Related Articles
View all posts security
securityWhat is Samsung SmartSwitch and Why It’s Essential for Device Migration
Migrating from one smartphone to another can be a time-consuming process filled with details: copying contacts, transferring photos, reinstalling apps, and restoring configurations.
 mdm
mdmDecoding the Android XR Platform: What IT Leaders Need to Know
Explore the new Android XR platform for enterprise. Learn about future device management capabilities, security protocols, and industry use cases to prepare your IT strategy.
